Polish “Space” GNSS Component Radiation Test Programme in its Final Stage

Astri Polska company has just finalized the last stage of radiation testing pertaining to the AGGA-4 advanced integrated circuit which is the key component of the GNSS receivers designed for space applications. The component was exposed to protons, while its operation was being monitored with the use of hardware and software designed by the Warsaw-based company. The test programme has been assigned to Astri by ESA.
AGGA-4 is an advanced integrated circuit designed for space applications. Primarily, it is being used as one of the main elements of the GNSS space satellite navigation receiver. The circuit is based on the ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) technology. This makes the component immensely efficient, since it acts as a system designed to carry out a specific task. In the nearest future the AGGA-4 ASIC would be used as a part of the satellite navigation receivers integrated with Earth Observation, navigation or telecommunication satellites, as well as with launch vehicles.
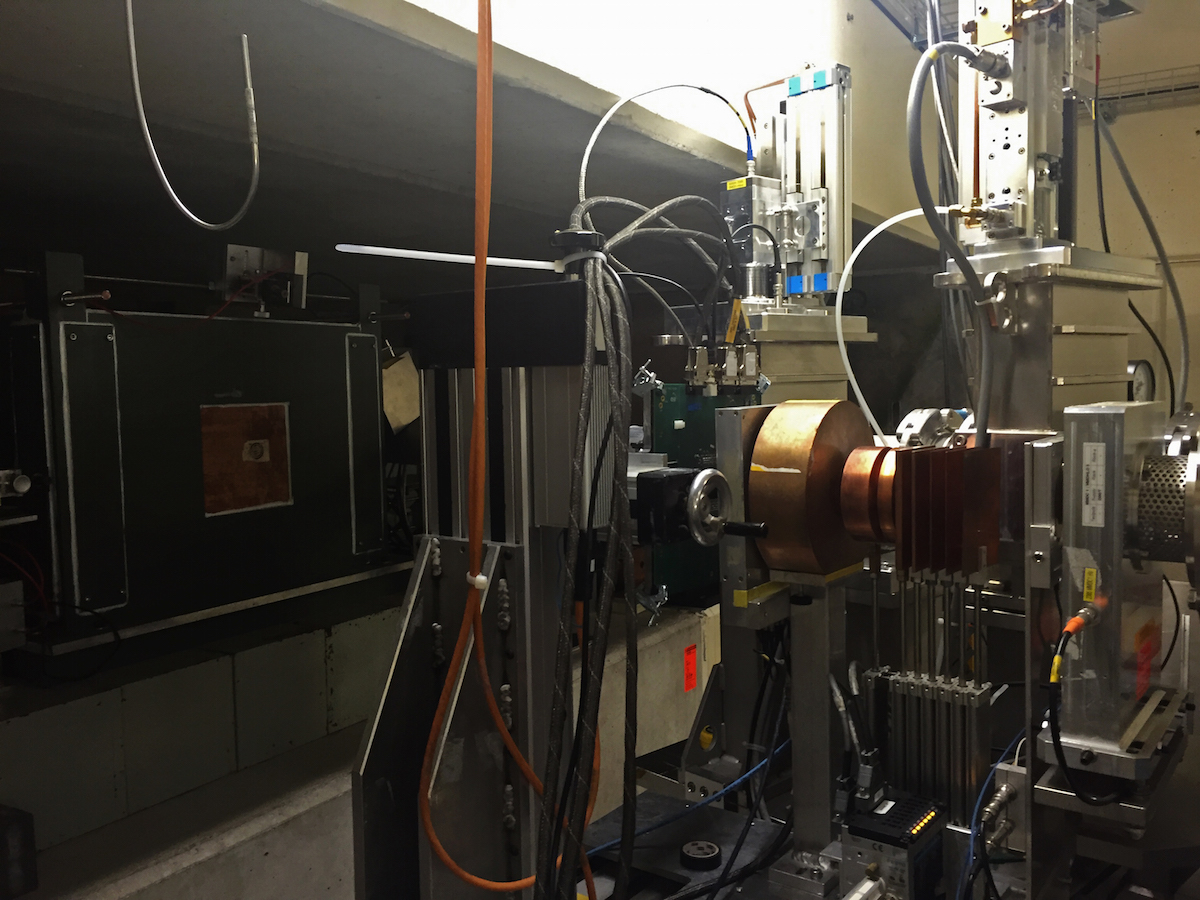
The test programme in question is aimed at verifying the operation of the AGGA-4 circuitry, when exposed to space radiation (cosmic rays), heavy ions and protons specifically. During all of the stages of the test programme, operation of the AGGA-4 system would be monitored by systems and software delivered by Astri Polska. Last weekend, during the phase II of the radiation tests (stage one took place at the end of February, at the Belgian Université Catholique de Louvain; back then, AGGA-4 was exposed to heavy ions) that took place at the Swiss Paul Scherrer Institute, the circuitry was exposed to protons.
We have managed to collect a lot of valuable data during the radiation test programme, pertaining to the operation of the AGGA-4 circuit. At the moment the consortium we lead is starting the data analysis stage which is to be followed by issuing of the final test report. Passing the document to ESA and subsequent approval issued by the technical officer would formally bring the project to a closure. It is worth to stress the fact that the results of our research, alongside testing the AGGA-4 circuit itself, would also provide us with numerous important pieces of information, useful for the space industry engineers and designers.
Astri Polska is the sole Polish company being in possession of expertise required to test the GNSS receivers designed for space applications. By the end of this year the company planned to deliver 10 readymade products to ESA. This is a record-breaking year within that regard, which is also distinguishing Astri Polska as a company, domestically and regionally. At the moment the entity is involved in 20 projects related to development of space and satellite technologies in the area of electronics, optomechatronics and satellite applications and services, mostly implemented for ESA.
Source: Astri Polska
