Industry
KenBIT’s Offer In The Polish ROSOMAK BMS Tender
Polish KenBIT company, offering the HEKTOR BMS system, has been qualified by the Armament Inspectorate to participate in the tendering procedure, the aim of which is to select the contractor that would deliver the battalion-level battlefield management system for the Polish Army, also known as “ROSOMAK BMS”.
HEKTOR is a system which is classified as a BMS class suite (Battlefield Management System). The suite supports the combat operations up to the battalion level. However, HEKTOR BMS suite may be expanded. With the use of proper means of communication it may be easily tailored for use at higher levels of the chain of command.
HEKTOR BMS is a completely mobile suite, providing the officers working at a variety of levels, within the chain of command, with capabilities as follows:
-
Directing the operational activities undertaken by the commanded forces;
-
Creating the battlefield situational awareness, e.g. through visualizing the positions of own and enemy forces on a digital map.
According to the assumptions, HEKTOR BMS is tailored to the needs of the Land Forces and special forces, also offering an option of providing an information exchange among the allies. HEKTOR’s software has already been implemented and is being used by two elements of the Polish Armed Forces.
The suite is also being updated, in an ongoing manner, in line with the latest NATO standards. HEKTOR BMS capabilities are being continuously verified in practical applications, during a variety of military exercises, such as Combined Endeavor, CWIX (Coalition Warrior Interoperability eXploration) and ASTER. This makes it possible to carry out credible tests, involving numerous partners, and to confirm proper implementation of the interoperability standards, used within the area of tactical information exchange.
Thanks to the above initiatives we already know that HEKTOR BMS may be, without any significant problems, work in connection with other allied systems, using the following protocols: MIP (Multilateral Interoperability Programme), NFFI (NATO Friendly Force Information), NVG (NATO Vector Graphics), MS (Web Map Server) and XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol). As it is stressed by the representatives of the manufacturer, a large part of the tests and verifications, carried out during the test programme of the HEKTOR BMS suite, had a positive result.
What are the elements of the HEKTOR BMS?
HEKTOR battlefield management system consists of five main components:
-
Planning and management subsystem, making it possible to configure and monitor the whole suite, locally and remotely;
-
Communications subsystem, making it possible to use all of the available communications media, create radio VHF/HF bridges between digital and analogue recipients within the telecommunications networks, realize connections with the JRS subsystem users (Jednokanałowy Radiodostęp Simpleksowy – Simplex Single Channel Radio Access), and WRS VHF subsystem users (Simplex Multi-Channel Radio Access), and for establishing phonic connections and data exchange between the wire-connections users (STORCZYK, ISDN, H.323) and HF/VHF users;
-
Data exchange subsystem, making it possible to establish communication nodes with the individual command vehicles of the combat unit, allowing them to: Automatically retransmit the information from the sender to the recipient, via all the media; automatically exchange the data, with search for the ways of delivering the messages within all of the communications media and implement MEMs (Message Exchange Mechanisms) and DEMs (Data Exchange Mechanisms) of the MIP programme;
-
Encryption Protection Subsystem, making it possible to safely exchange the “Restricted” confidential information, along with authentication of the users, when the information is passed on, outside the protection zones;
-
Command, control and monitoring subsystem.
The command, control and monitoring subsystem makes it possible to:
-
Gather the information and dynamically visualize the tactical situation,
-
Graphically work on a multi-layered digital map,
-
Visualize the tactical situation within the digital map, along with the current location of the command vehicle, on the basis of the data provided by the Global Positioning System,
-
Visualize the information gathered during the reconnaissance, within the digital maps of the automated operator stations;
-
Position the elements of the combat unit, for the purpose of visualizing the battle situation in real time,
-
Autonomously realize command functions within all of the phases of tactical operations, starting from the individual soldiers, up to the Division level,
-
Command “two levels down”;
-
Take over or transferring the command by other person nominated as a post holder;
-
Separate of command and communications functions (commander, thanks to this, is not absorbed by the communications);
-
Realize authorized exchange of the battle documents;
-
Transfer and preparation (group work) of command documents;
-
Cooperate with the SZAFRAN ZT system (provision of data for the SZAFRAN ZT suite databases);
-
Transfer the ABC weaponry alerts and critical information;
-
Plan the tactical operations;
-
Exchange of the logistics information;
-
Transfer the imagery;
-
Implement the automated general military reconnaissance functions (reporting on detected targets);
-
Transfer the information to the fire control systems (e.g. TOPAZ, AZALIA, LOARA);
-
Carry out the operations related to the automated engineering reconnaissance functions (gathering the information and reporting);
-
Direct the Electronic Warfare activities (cooperation with the PRZEBIŚNIEG, PROCJON or BREŃ suites).
HEKTOR BMS features a properly selected ICT infrastructure, along with a number of ICT devices making it possible for the suite to be operated on the vehicular platforms, such as the Rosomak APC. Besides that, the system also included software in two variants: for onboard terminals and for personal/PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) terminals, for the individual soldiers.
Both the software, as well as the ICT hardware suite of the Hektor BMS, provide the following capabilities:
-
Cooperation with the navigation systems and a variety of communications systems (broadband IP radios and personal IP radios, narrowband HF and VHF radios and tactical satellite terminals);
-
Cooperation with other elements of the field ICT system operated by the Polish Army: ZT STORCZYK 2000 Digital Radio-Wired Communications System, ZWT KTSAwp3 JAŚMIN, PPTS FIKUS (Portable Satellite Terminal);
-
Interoperability with other NATO units, within the framework of information exchange.
Hektor BMS System Software
HEKTOR BMS software installed on PC-class computers, servers and personal PDA-class terminals are based on technologies rarely applied in the Polish Army: New generation Java language, along with a variety of other new components, such as the JBoss application server, EJB technology, Framework Hibernate, JAAS, Oracle.
HEKTOR suite features two main modules:
-
Software for the Battlefield Management Suite;
-
Software for the Blue Force Tracking module.
BFT Software is destined to be used with the combat identification and information exchange suite, making it possible to track own forces within the battlefield. BFT module is created in a way which makes it possible to install it independently from the HEKTOR BMS, and it is implemented in two variants: for onboard and PDA-based terminals.
BMS Software, thanks to its modular structure, makes it possible to:
-
Create specialized work stations, with a variety of levels of responsibility;
-
Create new functions, meeting the growing demands, should new data exchange standards be implemented.
The system may work independently, or in a distributed manner which greatly enhances its efficiency, by initiating the individual modules and services, such as MIP, map server etc. on separate machines within the whole network. The BMS software also features a Polish/English user interface. There is also an option of applying a touchscreen interface, tailored for night- and daytime use.
BMS module utilizes the latest NFFI mechanism, along with normalization of the MIP programme, including the MIP DEM Baseline 3.0 and 3.1 mechanisms. This makes it possible to create a hierarchical information structure, with the use of catalogue services complying with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), covering the battle group and network resources, with the structure being defined in the Battlefield Directory service, compliant with the STANAG 4644 and ACP 133(D) memorandums.
The functions provided by the BMS software support the tactical operations of the elements (e.g. at the battalion level), they make it possible to record the operational data and conversations within the whole scope of internal and external communications.
HEKTOR BMS Software Architecture
The HEKTOR software suite is based on a “client-server’ architecture, consisting of the core and modules which enable the user to tailor the software functionality to the work station at which the software is to be applied.
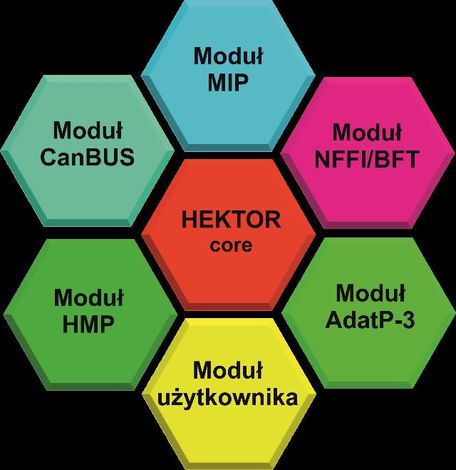
The engine is responsible for general configuration of the system, authorization of the users, it also makes it possible to integrate the attached modules, used depending on the existing needs:
-
ADat-P3 module (Allied Data Publication No 3) - dealing with the messages composed with the use of the formalized command language, automating the data exchange, inter alia, within the following scope: OWNSITREP (Own Land Forces Situation Report) and ENSITREP (Enemy Situation Report), along with the CFF (calls for fire);
-
“CANBUS” module, gathering the information from systems and sensors within the vehicle, including: GPS, compass, engine sensors, laser sensors, etc.;
-
GW HMP (Gateway Hektor Messaging Protocol) Module – Data exchange protocol dedicated for the low bandwidth networks. Exchanges the information with the use of the Radio Replication Mechanism for the radio interface. In conjunction with the Tactical Information Converter, the system makes it possible to exchange the JC3IEDEM model data at the tactical level, with the use of radio communications.
-
GW MIP DEM 3.0 (Gateway Multilateral Interoperability Programme) module – provides interoperability with suites of the same class via the DEM 3.0 (Data Exchange Mechanism) protocol;
-
GW MIP DEM 3.1 (Gateway Multilateral Interoperability Programme) module – provides interoperability with suites of the same class via the DEM 3.1 (Data Exchange Mechanism) protocol;
-
GW MIP ADEM 1.0.6 (Gateway Multilateral Interoperability Programme) module – provides interoperability with suites of the same class via the ADEM 1.0.6 (Alternative Data Exchange Mechanism) protocol;
-
HCHAT module – makes it possible to exchange text messages via the XMPP protocol;
-
LDAP module – used to store the hierarchical information structure, covering the battle group, network resources and data required to authorize the users;
-
MIP 3.0 module – user interface with visualization of the tactical situation stored within the JC3IEDM 3.0 (Joint Consultation, Command and Control Information Exchange Data Model) database;
-
MIP 3.1 module – user interface with visualization of the tactical situation stored within the JC3IEDM 3.1 (Joint Consultation, Command and Control Information Exchange Data Model) database;
-
NFFI module – used to transfer the information pertaining to positions of own and allied forces. HEKTOR BMS also provides interoperability with systems of the same class, through exchange of the information via the following protocols: IP1, IP2, SIP3;
-
NVG Module – Dealing with the NVG standard data (NATO Vector Graphics). Within the system, this module is used to exchange the information pertaining to the battlefield tactical situation awareness, and creation of a Joint Image of Operational Situation;
-
“POKŁADY MAP” module – makes it possible to display the requested maps, it may use the following data sources: CADRG files, DTED files, SHP files, S57 files, GeoTIFF files, WMS server, WFS server;
-
“ZNAKI TAKTYCZNE” module – provides visualization of tactical signs and symbology on the digital maps (point and area symbols). The plug-in in question supports the APP-6A standard expanded with the MIP symbols;
-
“SOL” module – makes it possible to visualize the information delivered by the SOL system (laser warning receiver);
-
“OBRA” module – making it possible to display the status of the OBRA self-defence system mounted on the vehicle, visualizing the status of the individual components of the system and directions at which the radiation is received.
Interoperability with other suites
According to the KenBIT company, the software used within the HEKTOR BMS system, makes it possible to use all of the standard NATO communications norms and protocols, allowing the user to:
-
Provide the information feed for the process in which the COP/JCOP tactical visualization is prepared, with the use of the JIPS (JCOP Information Product Service) protocol;
-
Map the data according to the NVG format data standard (NATO Vector Graphics);
-
Share the data in the NVG JPS format.
HEKTOR BMS software makes it possible to visualize the tactical situation, including movement tracks, current positions of own forces and tactical objects located within the area of operations, with the use of the standard APP-6(A) and APP-6(B) military symbols for the digital maps, with application of digital vector and raster graphics.
Within that software suite, arrangements contained within the STANAG 5500 (ADatP-3 Baseline 11-14) document. This includes automatic generation, transfer and processing of the following messages: OWNSITEREP, ENSITREP, FM.CFF (Fire Mission – Call for Fire), INTREP and Contamination Reports: CBRN4, CBRN3 i CBRN5 (Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear).
Thanks to the above capacities, HEKTOR BMS allows the user to:
-
Call for unarmed or armed medical transport unit: MEDEVAC and CASEVAC messages,
-
Determine the Fresnel zones (radio signal propagation areas) with the use of the DTED (Digital Terrain Elevation Data) profile;
-
Calculate the sunrise/sunset/moonrise/moonset times for the selected location;
-
Maintain an electronic battle diary.
BMS HEKTOR ICT Infrastructure
Hektor BMS suite includes a bundle of ICT devices dedicated to be used onboard the armoured vehicles, making it possible to implement the required communications and command functionalities. Vehicles equipped in this way constitute so called HEKTOR BMS objects.
Depending on the level and tasks carried out, different variants of the above may be used which may feature commander/deputy commander stations at the company and battalion level, commander stations for platoon and team commanders, station for the chief of staff and the officers, and a station for the crew commander. These stations make it possible to exchange the information both within the vehicle, as well as with the supervisors and the cooperating elements, both in a stationary setting, as well as on the move. There is also an option of working outside the vehicle, with the use of portable stations.
The ICT systems embedded within the vehicle provide encrypted direct data exchange and communications capability, within the framework of the inter-level chain of command relations, also making it possible to connect the system to the field ICT network.
Each of the HEKTOR BMS objects (depending on the level at which this object exists) also provides the user with an option of operating within wireless IP, broadband and narrow band, networks, created out of the building blocks formed by the tactical broadband and narrowband radios and tactical satellite terminals. The devices that belong within the suite meet the requirements of the NO-06-A101 i NO-06-A103 standards for the N.11-O-II-A7 groups, while the portable modules meet the N.14-O-II-A group requirements.
Digital internal communications suite applied within every object of the HEKTOR BMS system allows the user to:
-
Carry out voice connections, data transmission and VoIP voice connectivity within the vehicle; establish encrypted connectivity between the vehicles of the battalion battle group and the objects of the cooperating battalions,
-
Control the onboard radio communication devices,
-
Permanently receive and send alerts and other urgent messages, regardless of the terminal’s mode of operation.
HEKTOR BMS architecture allows for quick change of the function of the command vehicles, both through reconfiguration of the software, as well as through installation of a relevant communications system onto the vehicle. The work undertaken by the officer at the station, within the given platform, is limited to redefinition of the HEKTOR BMS access authorization levels. Whereas the software structure makes it possible to change and update the individual modules, without having to reinstall the whole software suite.
Onboard communications
Each of the HEKTOR BMS vehicles/objects is equipped with the following means of communications:
-
1-2 VHF radios (quantity depending on the variant);
-
1 HF radio;
-
1 broadband IP onboard radio,
-
1 broadband personal IP radio – base station;
-
1 WLAN module (Wireless Local Area Network).
HEKTOR BMS-equipped vehicles are additionally fitted with autonomous navigation devices making it possible to operate the suite on the move and when the host platform is stopped. The navigational component includes INS system which is fully integrated with an external military-grade GPS suite, using the SAASM module.
HEKTOR BMS software uses the standard TCP/IP and UDP/IP protocols (respectively for broadband and narrowband networks), also during the radio transmission. In the light of the fact that the system operates in tough conditions at the tactical level, with possible interruptions of data transmission, the BMS software is fitted with a RRM mechanism, making it possible to automatically transfer the information selectively, compress the data, send the prioritized data packages, with simultaneous assurance that the data integrity is maintained. RRM makes it possible to divide the information into segments and send the data packages via a variety of radio communication systems, optimizing the time period within the information is exchanged, according to MIP DEM Baseline 3.0 and MIP ADEM Baseline 3.1).
For the purpose of providing data transmission via the HF radio, the ICT subsystem may be operated in line with the STANAG 5066 and STANAG 4538 requirements. Moreover, QoS (Quality of Service) function is embedded within the system, operating at the application level, applying a hierarchy of importance of the transmitted information, ascribing proper priorities to the individual users or data packages.
Hektor system may cooperate in conjunction with the following communication devices:
-
WLAN module that is used to create WLAN infrastructure and wireless networks;
-
Wireless IP telephone, used to cooperate within the WLAN module (using the wireless IEEE 802.11 b/g/n standard connections);
-
Onboard VoIP terminal, used to carry out internal HEKTOR BMS object communications, and for external communications via the vehicle-borne transmission devices.
-
IP RED integrator, making it possible to connect and integrate active devices behind the encryption device (e.g. packages of computer workstations, VoIP terminals, vehicle sensors, microphone/headsets for the officers);
-
IP BLACK integrator, making it possible to connect and integrate the active devices in front of the encryption device (e.g. broadband and narrowband radios, satellite terminals, narrowband radios, WLAN modules);
-
WSP-1 Portable Workstation – external portable communications terminal, making it possible to establish wireless communication and IP data exchange with the base vehicle. Along with the attached PC terminal, this module provides full access to the functions of the command vehicle.
-
WSP-2 Portable Workstation – external, portable device that may be used as a router or as a switch. The device is used to secure the operation of remote work locations via the PKL 1x2 field cable and field fibre optics. This component makes it possible to establish local Ethernet networks, in the field.
-
Broadband IP radio that may be embedded within a mobile platform. This element uses broadband modulation and technologies related to dispersion of the signal spectrum in the frequency domain, camouflaging and sharing the bandwidth. Such radio makes it possible to organize a radio communications suite with additional protection of the broadband data exchange from the team level upwards, providing the tactical commanders with command and data exchange capabilities in stationary settings and on the move;
-
Computerized workstation which may come in a form of a computer terminal which may be installed on the BMS HEKTOR objects (with an option of moving the terminal outside the object), or personal, PDA-based, terminals that may be used by the soldiers who leave the vehicle.
Encryption protection subsystem
The encryption protection subsystem is a software-hardware solution encrypting the confidential information exchange realized within the HEKTOR BMS. This subsystem includes the following elements:
-
Radio encryption modules;
-
Encryption management stations;
-
Encryption data carriers;
Encryption Protection Subsystem, makes possible to safely exchange the “Restricted” confidential information, along with authentication of the users, when the information is passed on, outside the protection zones. This module also provides the user with a capability of securing the information processed within the ICT environment in national and allied settings, by provision of an option of implementing encryption algorithms provided by domestic or allied security bodies.
The information contained within the HEKTOR BMS software is protected from unauthorized access, modification or destruction. At the same time, integrity and confidentiality of the said information is also provided. The information may be accessed, accounted for, it is reliable and it cannot be negated.
The above article has been prepared on the basis of the materials provided by the KenBIT Sp. J. company.








